1. Identifier
The first character must be an alphabet or underscore字母_
The rest of the identifier consists of.字母、下划线和数字
Identifier differentiation.大小写
2. Reserved words
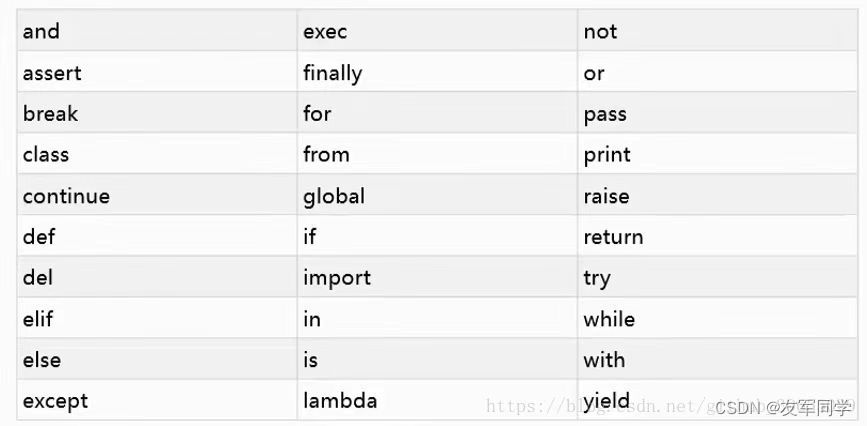
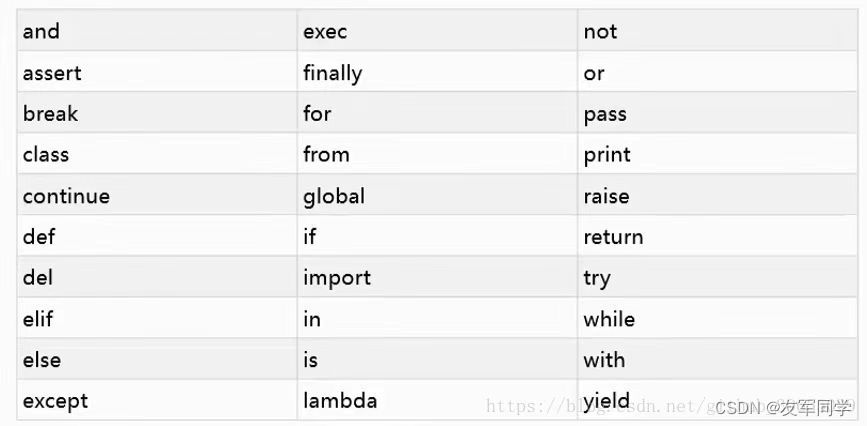
import keyword
print(keyword.kwlist)
”’
[‘False’, ‘None’, ‘True’, ‘and’, ‘as’, ‘assert’, ‘break’, ‘class’, ‘continue’, ‘def’, ‘del’, ‘elif’, ‘else’, ‘except’, ‘finally’, ‘for’, ‘from’, ‘global’, ‘if’, ‘import’, ‘in’, ‘is’, ‘lambda’, ‘nonlocal’, ‘not’, ‘or’, ‘pass’, ‘raise’, ‘return’, ‘try’, ‘while’, ‘with’, ‘yield’] hmi panel touch
3. Comments
In Python, single-line comments are used, and multi-line comments are used with three single quotation marks or three double quotation marks#”'”””
What comments do:
use a language you’re familiar with, annotate certain code in your program,增强代码的可读性
This is shown below:
# 单行注释 (为了保证代码的可读性,`#` 后面建议先添加一个空格,然后再编写相应的说明文字)
”’
多行注释
多行注释
”’
“””
多行注释
多行注释
“””
4. Multi-line statements
Python usually writes one statement in one line, but if the statement is too long, you can use a backslash to implement a multi-line statement.
For example:\
a = b + \
c + \
d
# 等价于
a = b + c + d
In multiline statements, you do not need to use backslashes(), [], {}\
For example:
temp = [‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’,
‘d’, ‘e’]
5. Print output
Print output Yes, if you need to implement no line breaks, you can add parameters at the end:默认换行end=””
a = 1
b = 2
print(a)
print(b)
print(‘———‘)
# 不换行输出
print(a, end=” ” )
print(b, end=” ” )
The output is as follows:
a = 1
b = 2
print(a)
print(b)
print(‘———‘)
# 不换行输出
print(a, end=” ” )
print(b, end=” ” )
6, import and from… import
Use sum in Python to import the corresponding moduleimportfrom…import
Import the entire module (somemoudle) in the following format:import somemoudle
Import a function from a module in the following format:from somemoudle import somefunction
Import multiple functions from a module in the following format:from somemoudle import firstfunc, secondfunc, thirdfunc
Import all functions from a module in the following format:from somemoudle import*