1. Redis implements friend follow-follow and unfollow
Requirements: According to the user’s operation, the user can follow and unfollow the function.
On the details page of the store’s pictures and texts, you can follow the author who posted the note
Specific implementation ideas: Based on the data structure of the table, implement 2 interfaces
Follow and unfollow interface
Determine whether to pay attention to the interface
Follow is the relationship between users, the relationship between bloggers and fans, the data table is as follows:
tb_follow
CREATE TABLE `tb_follow` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT ‘主键’,
`user_id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT ‘用户id’,
`follow_user_id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT ‘关联的用户id’,
`create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT ‘创建时间’,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=9 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 ROW_FORMAT=COMPACT;
id is self-growth, simplifying development
core code
FollowController
//关注
@PutMapping(“/{id}/{isFollow}”)
public Result follow(@PathVariable(“id”) Long followUserId, @PathVariable(“isFollow”) Boolean isFollow) {
return followService.follow(followUserId, isFollow);
}
//取消关注
@GetMapping(“/or/not/{id}”)
public Result isFollow(@PathVariable(“id”) Long followUserId) {
return followService.isFollow(followUserId);
}
FollowService
@Override
public Result follow(Long followUserId, Boolean isFollow) {
// 1.获取登录用户
Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();
String key = “follows:” + userId;
// 1.判断到底是关注还是取关
if (isFollow) {
// 2.关注,新增数据
Follow follow = new Follow();
follow.setUserId(userId);
follow.setFollowUserId(followUserId);
boolean isSuccess = save(follow);
if (isSuccess) {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add(key, followUserId.toString());
}
} else {
// 3.取关,删除 delete from tb_follow where user_id = ? and follow_user_id = ?
boolean isSuccess = remove(new QueryWrapper<Follow>()
.eq(“user_id”, userId).eq(“follow_user_id”, followUserId));
if (isSuccess) {
// 把关注用户的id从Redis集合中移除
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().remove(key, followUserId.toString());
}
}
return Result.ok();
}
@Override
public Result isFollow(Long followUserId) {
// 1.获取登录用户
Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();
// 2.查询是否关注 select count(*) from tb_follow where user_id = ? and follow_user_id = ?
Integer count = query().eq(“user_id”, userId).eq(“follow_user_id”, followUserId).count();
// 3.判断
return Result.ok(count > 0);
}
The code is written and tested
code testing
Click to follow users

Followed
unsubscribe

test was successful
2. Redis implements friend follow-joint follow function
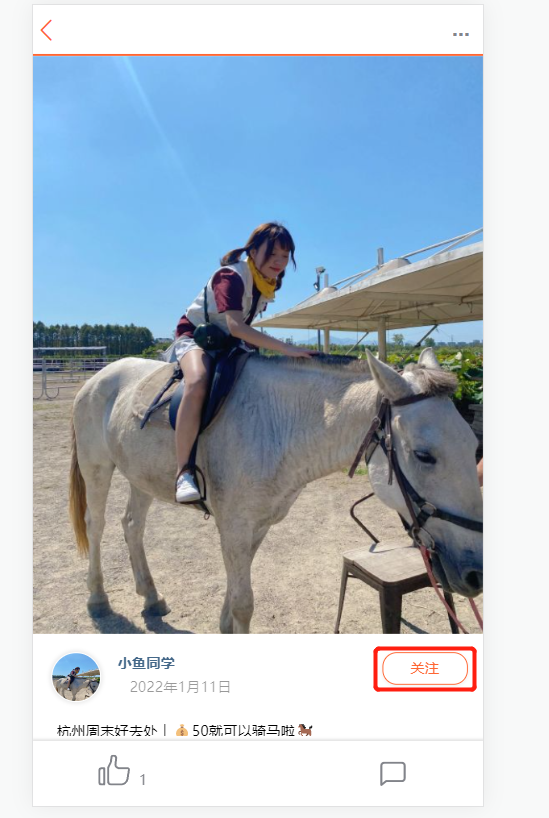
To achieve the function of following friends together, first, you need to enter the specified note page published by the blogger, and then click the blogger’s avatar to view detailed information
The core code is as follows
UserController
// UserController 根据id查询用户
@GetMapping(“/{id}”)
public Result queryUserById(@PathVariable(“id”) Long userId){
// 查询详情
User user = userService.getById(userId);
if (user == null) {
return Result.ok();
}
UserDTO userDTO = BeanUtil.copyProperties(user, UserDTO.class);
// 返回
return Result.ok(userDTO);
}
BlogController
@GetMapping(“/of/user”)
public Result queryBlogByUserId(
@RequestParam(value = “current”, defaultValue = “1”) Integer current,
@RequestParam(“id”) Long id) {
// 根据用户查询
Page<Blog> page = blogService.query()
.eq(“user_id”, id).page(new Page<>(current, SystemConstants.MAX_PAGE_SIZE));
// 获取当前页数据
List<Blog> records = page.getRecords();
return Result.ok(records);
}
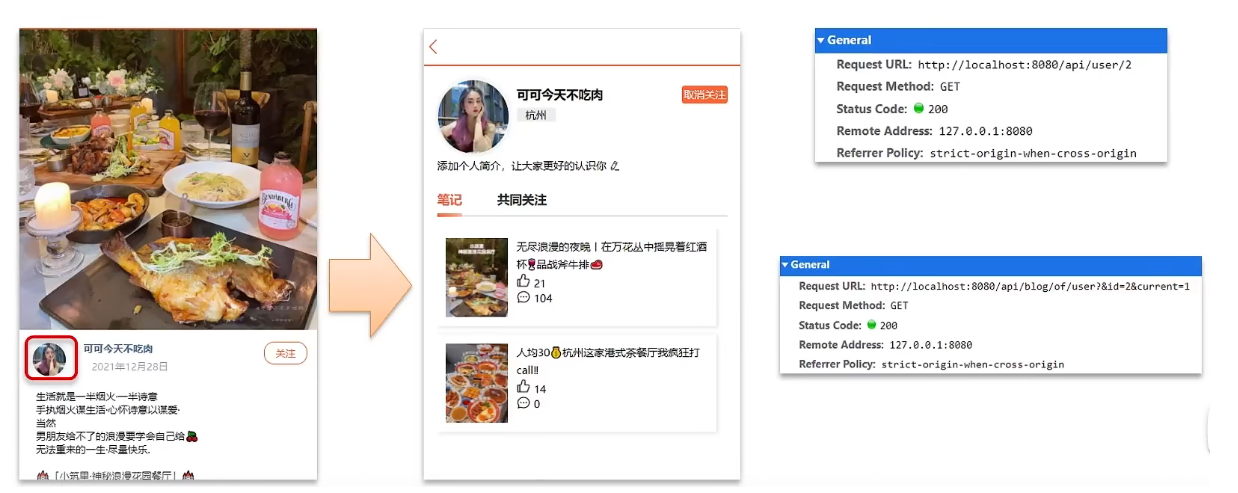
So how to realize mutual friend following function?
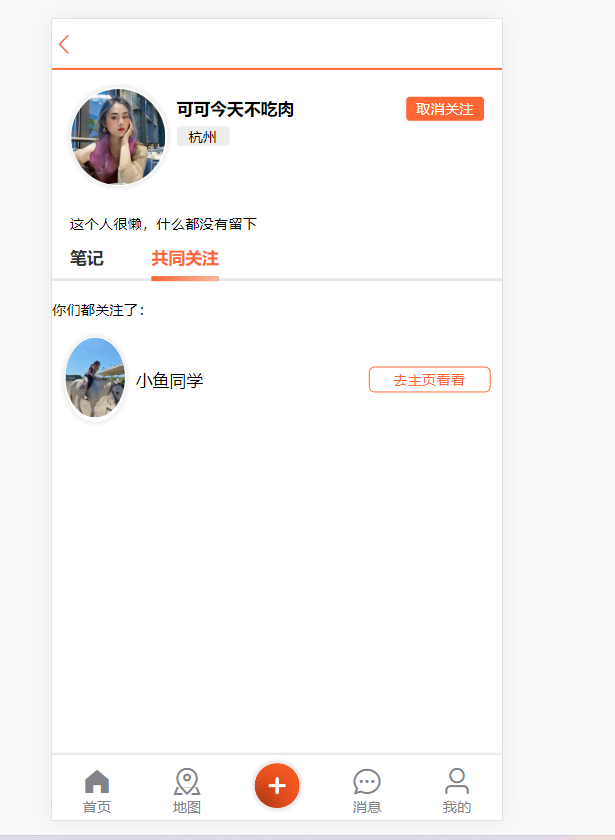
Requirements: Use the data structure in Redis to realize the common attention function. Display the common concerns of current users and bloggers on the blogger’s personal page
Idea analysis: Using the Set collection of Redis to implement, we put the people who the two people follow into a Set collection respectively, and then use the API to view the intersection data in the two Set collections
Transform the core code:
When a user follows a certain user, the data needs to be stored in the Redis collection to facilitate the realization of common attention in the future. When unfollowing at the same time, the collection in Redis needs to be deleted
FlowServiceImpl
@Override
public Result follow(Long followUserId, Boolean isFollow) {
// 1.获取登录用户
Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();
String key = “follows:” + userId;
// 1.判断到底是关注还是取关
if (isFollow) {
// 2.关注,新增数据
Follow follow = new Follow();
follow.setUserId(userId);
follow.setFollowUserId(followUserId);
boolean isSuccess = save(follow);
if (isSuccess) {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add(key, followUserId.toString());
}
} else {
// 3.取关,删除 delete from tb_follow where user_id = ? and follow_user_id = ?
boolean isSuccess = remove(new QueryWrapper<Follow>()
.eq(“user_id”, userId).eq(“follow_user_id”, followUserId));
if (isSuccess) {
// 把关注用户的id从Redis集合中移除
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().remove(key, followUserId.toString());
}
}
return Result.ok();
}
// 具体获取好友共同关注代码
@Override
public Result followCommons(Long id) {
// 1.获取当前用户
Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();
String key = “follows:” + userId;
// 2.求交集
String key2 = “follows:” + id;
Set<String> intersect = stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().intersect(key, key2);
if (intersect == null || intersect.isEmpty()) {
// 无交集
return Result.ok(Collections.emptyList());
}
// 3.解析id集合
List<Long> ids = intersect.stream().map(Long::valueOf).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 4.查询用户
List<UserDTO> users = userService.listByIds(ids)
.stream()
.map(user -> BeanUtil.copyProperties(user, UserDTO.class))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return Result.ok(users);
}
carry out testing